How To Find Size Of Vector C++
The dynamic assortment can be created past using a vector in C++. One or more elements can be inserted into or removed from the vector at the run fourth dimension that increases or decreases the size of the vector. The size or length of the vector tin be counted using any loop or the built-in function named size(). These ways of counting the size of the vector have been explained in this tutorial by using different examples.
Pre-requisite:
Earlier checking the examples of this tutorial, you have to check the g++ compiler is installed or not in the organisation. If you are using Visual Studio Lawmaking, so install the necessary extensions to compile the C++ source code to create the executable code. Here, the Visual Studio Code application has been used to compile and execute the C++ code.
Example-1: Count the size of the vector using a loop
Create a C++ file with the following code to count the size of a vector without using whatsoever built-in part. A vector of string values has been declared in the code. A user-defined function named calculate_size() has been declared hither to calculate the size of the vector using a loop. This office takes the vector as an argument value and returns the size of the vector to the caller. This function has chosen for the commencement time afterwards declaring the vector. Adjacent, two values have been added at the finish of the vector that will increase the size of the vector. The calculate_size() function has chosen for a second time to count the size of the modified vector.
//Include necessary modules
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
usingnamespace std;
//Declate part to calculate the size of the vector
intcalculate_size(vectorstrVec)
{
//Initialize a cord variable
int length = 0 ;
/*
Iterate the content of the loop
and increment the value of the length variable in each iteration
to count the size of the vector
*/
for (string chemical element: strVec)
length++;
//Render the size value
return length;
}
intmain( ) {
//Declare a vector of cord data
vector items = { "Book" , "Pen" , "Pencil" , "Eraser" } ;
//Print the current size of the vector
cout<< "The size of the vector is : " <<calculate_size(items) <<endl;
//Add ii new items using push_back() role
items.push_back ( "Color Paper" ) ;
items.push_back ( "H2o colour" ) ;
//Print the electric current size of the vector after improver
cout<< "The size of the vector after add-on is : " <<calculate_size(items) <<endl;
}
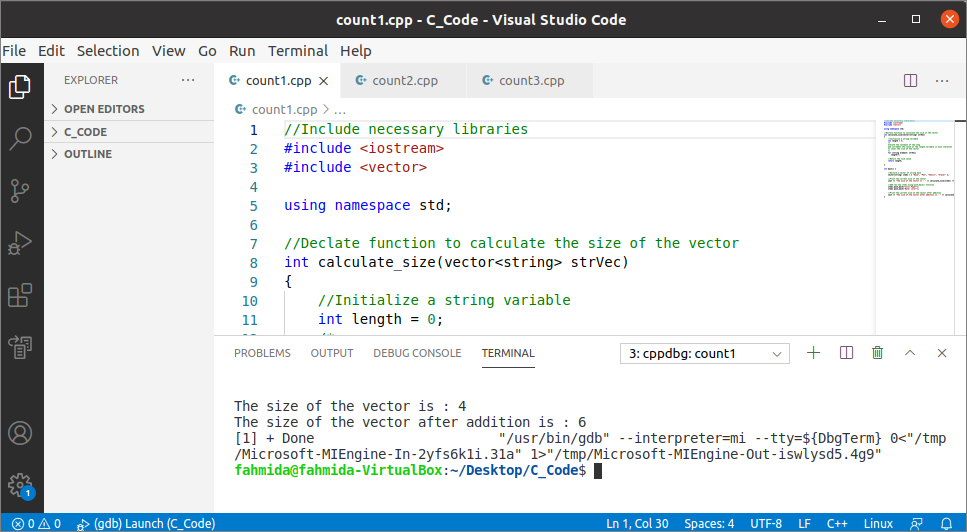
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code. At that place were 4 elements in the vector at the time of declaration. So, the output shows that the size of the vector is 4 before inserting the new values, and the size is vi later on inserting 2 values.
Example-2: Count the size of the vector using size()
The built-in function exists in C++ to count the size of the vector. The function name is, size(). It returns the size or the total elements of the vector in which vector it is used. It does not take whatever statement.
Syntax:
The post-obit example shows the utilise of the size() function to count the full elements of a vector. Create a C++ file with the following code to test the code. A vector of integer numbers has been declared in the code. The vector contains 8 elements at the fourth dimension of declaration. The size() function has been used the kickoff time to count the total elements of the vector and print the count value. The size() office has been used a second fourth dimension to count the total elements after adding four elements at the end of the vector.
//Include necessary modules
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
usingnamespace std;
intmain( )
{
//Declare a vector of integer information
vectorintVector{ 56 , 89 , 45 , 87 , 21 , 77 , ten , 42 } ;
//Print the size of the vector
cout<< "The size of the vector is : " <<intVector.size ( ) <<endl;
//Add together some values to the vector using push_back() part
intVector.push_back ( 65 ) ;
intVector.push_back ( 90 ) ;
intVector.push_back ( 49 ) ;
intVector.push_back ( 16 ) ;
//Impress the size of the vector after addition
cout<< "The size of the vector after addition is : " <<intVector.size ( ) <<endl;
return0;
}
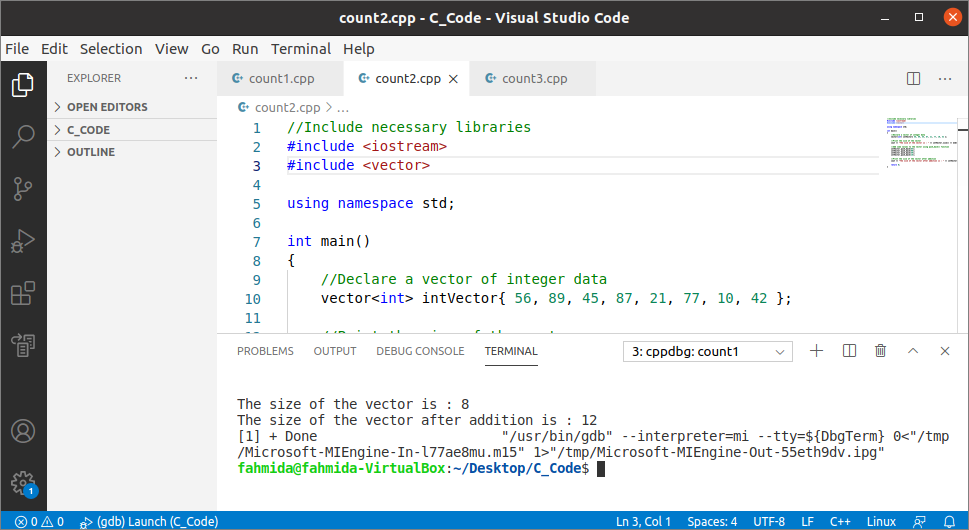
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above code. There were viii elements in the vector at the time of declaration. Then, the output shows that the size of the vector is viii before inserting the new values, and the size is 12 after inserting 4 values.
Case-iii: Count the size of the vector to insert fifty-fifty numbers
The following example shows how to insert 10 fifty-fifty numbers into the vector after defining the size of the vector. Create a C++ file with the following code to test the code. A vector of integer type with 10 has been declared at the get-go of the lawmaking. An integer variable has been declared to insert 10 fifty-fifty numbers from 0 to 18 into the vector. Here, the 'for' loop has been used to iterate the vector based on the returned value of the size() function and insert the element into the vector. Next, the output of the size() function has been used to print the vector's values.
//Include necessary modules
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int primary( )
{
//Declare a vector of ten elements
std:: vector <int> myArray( 10 ) ;
//Initialize an integer variable
int value = 0 ;
//Insert even numbers into the vector using size()
for ( int i = 0 ; i < myArray.size ( ) ; i++ )
{
myArray[i] = value;
value = value + two ;
}
//Print the values of the vector using size()
for ( int j = 0 ; j < myArray.size ( ) ; j++ )
cout << myArray[j] << " " ;
//Add together newline
cout << endl;
}
<strongusingnamespace std;
intmain( )
{
//Declare a vector of 10 elements
std:: vectormyArray ( 10 ) ;
//Initialize an integer variable
int value = 0 ;
//Insert even numbers into the vector using size()
for (inti = 0 ; i<myArray.size ( ) ; i++ )
{
myArray[i] = value;
value = value + two ;
}
//Print the values of the vector using size()
for ( int j = 0 ; j <myArray.size ( ) ; j++ )
cout<<myArray[j] << " " ;
//Add newline
cout<<endl;
}
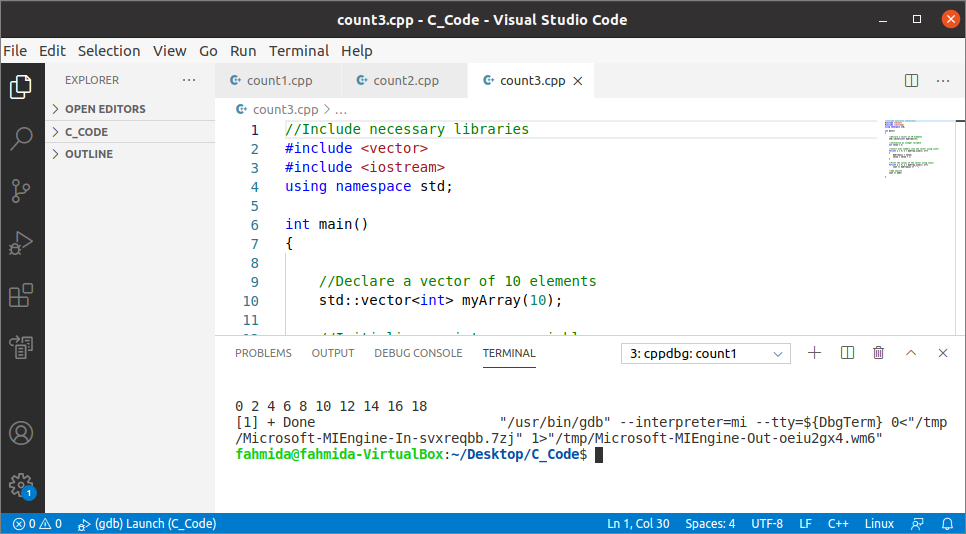
Output:
The following output will appear later executing the above code.
Conclusion:
Two different ways to count the total elements of a vector have been described in this tutorial using the vector of cord data and numeric data. The C++ user will be able to count the size of the vector using a built-in function or loop to solve different programming purposes subsequently reading this tutorial.
How To Find Size Of Vector C++,
Source: https://linuxhint.com/count-vector-size-c/
Posted by: jantzenprolead.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Size Of Vector C++"
Post a Comment